The Four C’s of Diamonds.
The Four C’s of diamonds are value factors which consist of a diamonds Clarity, Colour, Cut, and Carat Weight, each which describe the value of a finished diamond, and is directly related to its value.
Clarity:
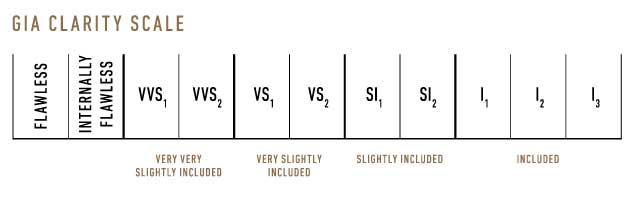
Clarity grading is one of the most important aspects of the diamond grading system. Clarity Characteristics are internal and external features (flaws and imperfections) of a gemstone that help determine its quality and establish its identity. Under 10x Magnification, most diamonds contain natural inclusions, or birthmarks which make each stone unique. Clarity is measured on a scale based on the number, size, position, and colour or relief and nature of a diamonds inclusions. Clarity is graded into eleven grades from Flawless (F) through obvious inclusions (I3).
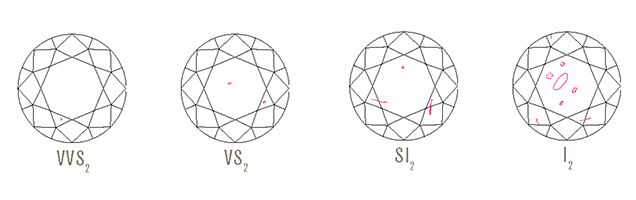
Colour:
Diamonds are graded on the GIA colour scale from D (Colourless) to Z (Yellow) based on their absence of colour. Although it is common misconception that colour in a diamond devalues it, the most expensive stones are those which are either completely colourless, or are highly coloured (Fancy Coloured). Coloured is divided into 5 categories: Colourless, Near Colourless, Faint, Very Light, and Light.
Fluorescence: Diamonds which emit light or glow when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Approximately 35 percent of gem-quality diamonds fluoresce when they’re exposed to ultraviolet radiation, most of which fluoresce blue. Diamonds with strong blue fluorescence are considered less desirable in the D-H Colour range as they give the stone a bluish tint, and in other circumstances when the colour range is between I-N, a strong fluorescence can give it a more colourless appearance.

Cut:
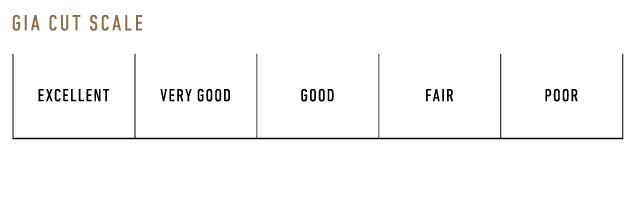
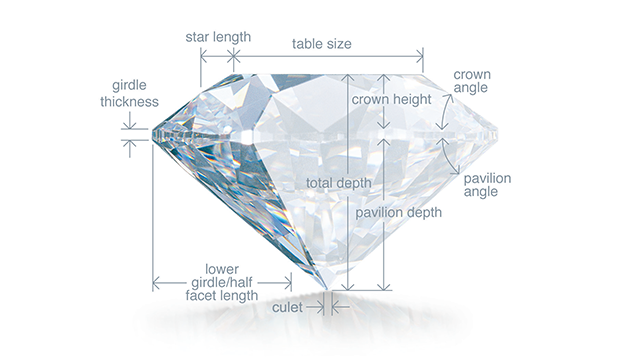
A diamonds cut has the greatest overall impact on the beauty of a stone, as its determines the overall brilliance, fire and scintillation of a diamond. A diamond’s brilliance is the brightness created by the combination of all the white light reflections from the surface and the inside of a polished diamond. Fire, are the flashes of colour you see in a polished diamond, while scintillation are the flashes of light you see when the diamond, the light, or the observer moves. A diamond cutter must use precision to make sure all aspects of the cut give maximum refraction of light. If a stone is cut too shallow, light will escape through the bottom of the stone, and if it is cut too shallow, light escapes from the side of the stone. Also the cut of the stone will have a large impact on the stones stability.
Carat Weight:
A carat is a unit of metric measurement used for gems. One carat (ct) equals 100 points or 1/5 of a gram.

